🌐💻 Internet History 🧠🚀
If you're fascinated by how the Internet came to be, its journey is filled with groundbreaking innovations that shaped the way we connect, communicate, and share information! 🌍
Starting with early visions of interconnected networks in the 1960s 🧠, the birth of ARPANET 🌐 in the 1969 set the stage for the rapid expansion of the Internet. In 1983, the adoption of TCP/IP protocols allowed different networks to communicate, laying the foundation for the modern Internet. By the 1990s 🌐, the World Wide Web 🌍 transformed the way we interact with online content, and the 2000s brought a new era of connectivity with social networks and the rise of high-speed broadband. Today, the Internet is an integral part of our daily lives, continuously evolving with the advent of mobile devices 📱 and the Internet of Things (IoT) 🌐.
Auto Scroll
1960s – Early Ideas 🧠💡

The 1960s were a pivotal decade in the development of modern computing and networking. During this period, visionaries like Paul Baran and Donald Davies laid the groundwork for what would become the internet as we know it today. 🌐
In particular, Paul Baran's work on packet-switching was revolutionary. This concept involved breaking data into small, manageable packets that could be transmitted independently and reassembled at their destination. This approach greatly improved the efficiency of data transmission, paving the way for the decentralized communication systems we rely on now. 💻📡
Simultaneously, Donald Davies was developing similar ideas at the National Physical Laboratory in the UK, which led to the creation of the first packet-switched network. His work provided critical insights into how computers could exchange information over long distances. These developments were originally intended for military and academic applications, but they would soon evolve into the foundational technologies behind today’s global internet infrastructure. 🎓🪖
While the technology in the '60s was still rudimentary, the ideas that emerged from this era have had an enduring impact. Today, almost every form of digital communication relies on the principles of packet-switching and interconnected networks. These early pioneers set the stage for the explosion of the internet in the following decades, transforming how we communicate, share knowledge, and interact with the world. 🌍📱
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
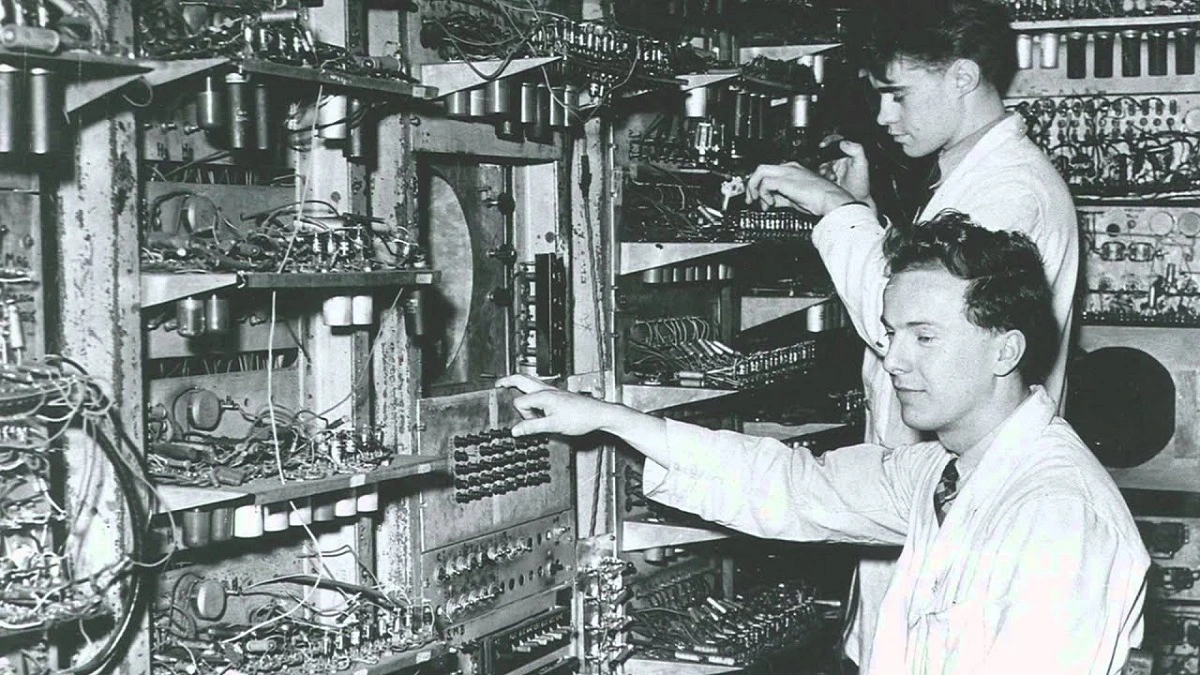
1960s – Birth of ARPANET 🌐🖥️
The late 1960s marked a revolutionary milestone in the history of computing and networking with the birth of ARPANET. Funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, ARPANET was initially a military project designed to connect different research institutions and government agencies. The primary goal was to create a robust communication system that could withstand potential threats, especially during times of war. ⚔️
ARPANET used a groundbreaking concept known as packet-switching, which allowed data to be broken into small packets and transmitted independently over the network. This method was far more efficient than traditional circuit-switched networks, as it allowed for more reliable and faster data transmission. 📡💨
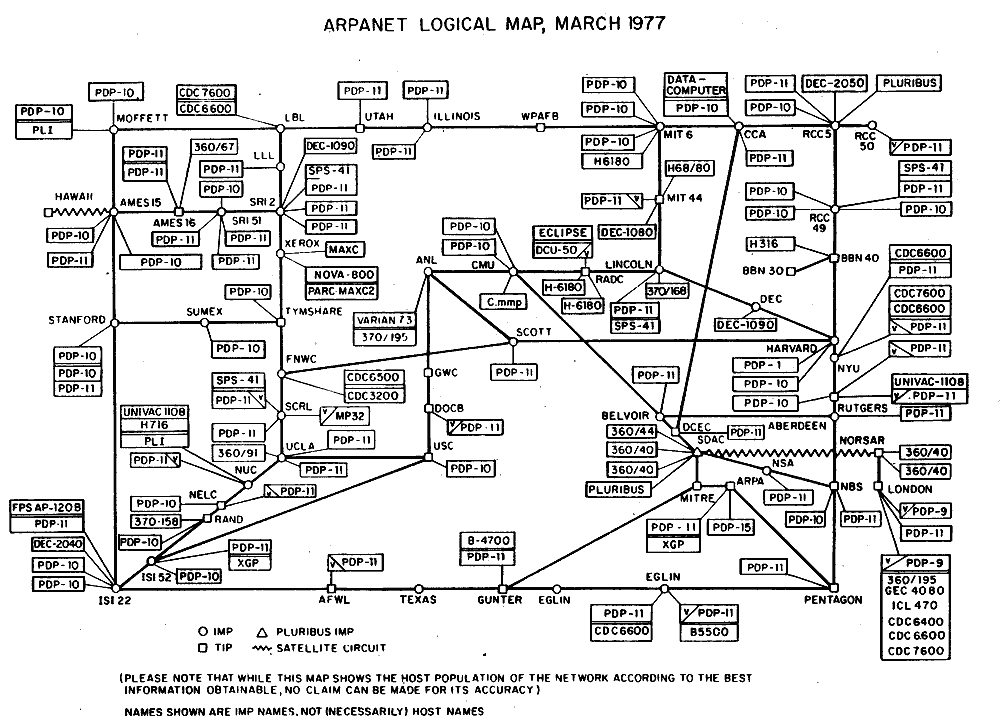
By connecting various academic and governmental institutions, ARPANET laid the foundation for what would become the modern internet. In 1969, ARPANET successfully connected four initial nodes: the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the Stanford Research Institute (SRI), the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), and the University of Utah. This marked the beginning of a new era in global connectivity. 🌍
While ARPANET was initially limited to academic and military use, its success inspired further development and eventually led to the growth of the global internet. By the early 1980s, ARPANET was expanded and evolved into a larger network that included commercial and non-profit organizations. Today, ARPANET's legacy lives on, as the principles it introduced remain at the core of the internet infrastructure we rely on today. 🌐🚀
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
1983 – Introduction of the TCP/IP Protocol 🔄📡
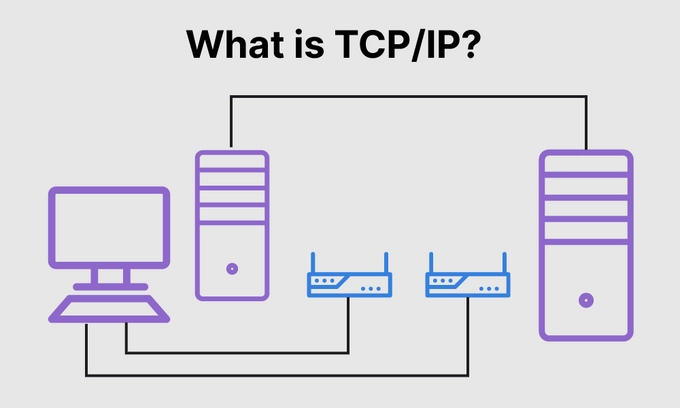
The year 1983 marked a critical turning point in the development of the internet with the adoption of the TCP/IP protocol by ARPANET and other networks. This shift standardized communication between computers, establishing a common language for data transfer across diverse networks. 🌐
Before TCP/IP, different computer networks were often isolated, each with its own method of communication. However, the introduction of TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) created a universal system that allowed networks to connect and exchange data seamlessly. 🔗💻
The protocol’s two key components—TCP, responsible for breaking data into packets and ensuring they arrive correctly, and IP, which handles the addressing and routing of these packets—became the foundation for all subsequent internet communications. 🚀💡
This innovation was not only vital for the continued growth of ARPANET but also for the global expansion of the internet. With TCP/IP, networks could now communicate with each other, regardless of their underlying technologies or geographical locations. This interconnectedness formed the backbone of the modern internet we use today. 🌍📶
By the mid-1980s, TCP/IP became the de facto standard for networking, and its adoption led to the rapid growth of the internet. As more networks switched to TCP/IP, the internet began to take shape as a truly global network, paving the way for the explosion of online services, websites, and applications that define our digital world today. 🌐📱
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
1991 – Birth of the World Wide Web 🌍📄

The year 1991 marked the dawn of a new era in the world of information technology with the invention of the World Wide Web (WWW) by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in Switzerland. 🌍💡
Prior to this invention, ARPANET had already connected computers and facilitated data sharing, but it lacked a user-friendly way to organize, access, and share documents. Berners-Lee’s revolutionary idea was to create a system that would allow people to view and interact with documents via hyperlinks, making the internet far more accessible and interactive. 🔗🖥️
Using HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), Berners-Lee developed a way for computers to link to each other and display documents on a web browser, creating a simple but powerful framework for accessing information. This combination of technologies gave birth to the Web as we know it today. 🌐📑
The first website, hosted at CERN, was a basic page explaining the concept of the World Wide Web and providing instructions on how to create your own website. While rudimentary by today’s standards, it laid the groundwork for the explosion of online content, from personal blogs to massive e-commerce platforms. 🖱️💻
The impact of the World Wide Web cannot be overstated. It transformed how we interact with information, enabling us to access a vast array of knowledge, connect with others globally, and participate in a digitally interconnected world. Since its introduction, the Web has revolutionized industries, education, communication, and entertainment. 🌍🚀
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
1990s – Global Expansion 🌐🚀
The 1990s were a pivotal decade for the growth of the internet, as it experienced an exponential expansion and started becoming a mainstream tool. 🌍💡 The foundation laid in the previous decades by ARPANET and the World Wide Web had ignited a revolution in communication, commerce, and entertainment.
As more people gained access to the internet, the web transformed from a niche technology used mainly by researchers and academics into a vital part of everyday life. Internet service providers (ISPs) proliferated, and home computers with dial-up connections became common. By the mid-90s, the internet was expanding rapidly across the globe, connecting people from all corners of the world. 🌎💻
During this period, the rise of popular web browsers like Microsoft Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator made navigating the web easier, allowing users to access websites and online content more efficiently. The advent of search engines such as Yahoo! and Google further enhanced the browsing experience, enabling users to find information faster and more accurately. 🔍🌐
By the end of the 1990s, the internet was no longer a novelty but a global communication and information network. However, the real transformation occurred at the dawn of the 2000s, with the emergence of Web 2.0. This new phase of the internet introduced a more interactive experience, where users not only consumed content but also created and shared their own through social media, blogs, and video-sharing platforms. 📱💬
The internet in the 1990s set the stage for the digital age we live in today. The global expansion of the web during this time paved the way for the rise of e-commerce, social networks, online entertainment, and countless other innovations that have reshaped how we connect, learn, work, and live. 🚀📈
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
2010s and Beyond – Mobility and the Internet of Things 📱🌐
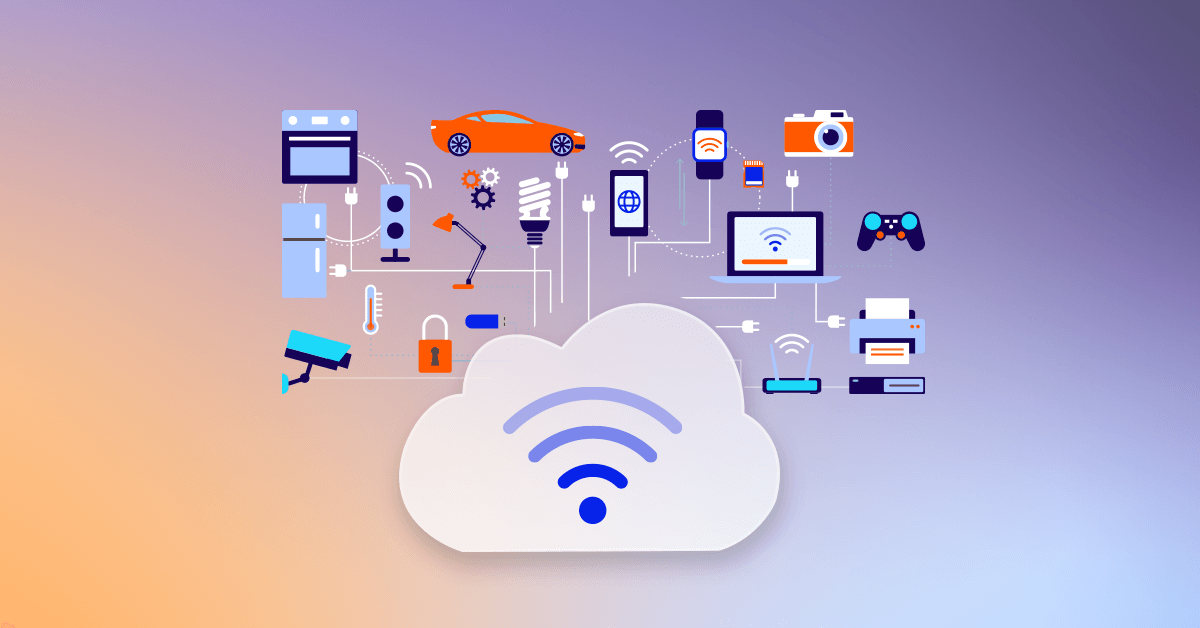
The 2010s marked a transformative era for the internet, as mobile technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) began to reshape our digital and physical worlds. 📱💡 During this decade, smartphones became ubiquitous, allowing people to access the internet, social media, and countless apps from virtually anywhere, revolutionizing communication, commerce, and entertainment. 🌍📲
As mobile internet usage surged, a new wave of connectivity emerged through the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and even wearable technologies that are connected to the internet and can exchange data. 🚗🏠 These devices communicate with one another, collecting and sharing data to make everyday tasks more efficient, such as monitoring health, managing smart homes, and optimizing transportation systems. 🌐🔌
One of the most significant advancements in IoT has been the rise of smart homes. With devices like voice-controlled speakers, smart thermostats, and connected security systems, people gained unprecedented control over their living environments, creating a more automated and personalized experience. 🏡🗣️
The IoT ecosystem also expanded into industries such as healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing, where connected devices improved productivity, monitoring, and data-driven decision-making. In healthcare, IoT-enabled devices, such as smartwatches and remote monitoring systems, have allowed for real-time health tracking and more personalized care. 🏥📊
While the benefits of IoT and mobile technology are vast, they also raise important questions about privacy and security. As more devices become interconnected, ensuring the safety of personal data and preventing unauthorized access have become critical challenges for both users and companies. 🔐💻
Looking to the future, the Internet of Things continues to evolve, with the promise of even more connected devices, smarter cities, and deeper integration of technology into our daily lives. As we enter a more connected and mobile world, the lines between the digital and physical realms will blur, creating opportunities for innovation and convenience. 🌍💡
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
Greetings and Thanks from the GWAP Staff 🤝🎉
We would like to thank everyone for the support and active participation in the GWAP community.
Each member is important and contributes to the team's success. We are proud of each one of you and the progress we make together.
Thank you for your dedication! We continue to learn and grow together, and our team spirit and mutual respect remain fundamental to our success.
We look forward to having you with us and are grateful for every moment spent in this wonderful community!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★











Comment on the article
You need to log in to comment.
Login
TEST1
Hai sus
TOPTOP!